| Millimetr-wave electron radiation sources and measuring complexes built around the above sources |
|
A) Klynotrons (O-type BWOs)
These devices whose function is to serve low- and medium power oscillators operating in the short-wave part of the millimeter wavelengths range find their wide use in physical experiment setups, radiospectroscopy, short-range radiolocation including radio-wave imaging.
The output radiation power is 1 W at a frequency of 150 GHz (2 mm). The klynotrons have a higher output signal power as compared to well-known BWOs. This type of a device has by now been developed featuring an enhanced power for the short-wave frequency band of 266 GHz.
Its parameters are as follows:
|
 |
 accelerating voltage U=4,8 êV accelerating voltage U=4,8 êV |
 current density in a beam j=50 À/ñm2 current density in a beam j=50 À/ñm2 |
 output power at 266 GHz P=250 mW output power at 266 GHz P=250 mW |
 combined frequency tuning over the band combined frequency tuning over the band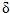 f=±2%f0 f=±2%f0 |
 focusing magnetic field B=0,8 T focusing magnetic field B=0,8 T |
 service life t=500 h service life t=500 h |
 dimensions (without magnets) S=50õ30 mm2 dimensions (without magnets) S=50õ30 mm2 |
 weight (without magnets) m=0.3 kg weight (without magnets) m=0.3 kg |
|
|
|
B) Diffraction radiation oscillators (DRO)
Novel DRO modifications have been developed:
specifically, pulse DRO-5 (electro-mechanical frequency tuning range is between 56 and 61 GHz), pulse DRO-3 (electro-mechanical frequency tuning range varies from 87 to 95 GHz), a small size pulse and continuous-wave miniaturized DRO-2 (electro-mechanical frequency tuning range is between 95 and 140 GHz). They are intended for use in coherent radars, spectroscopy of highly absorbing media, plasma diagnostics, for pumping nuclear targets. Below (see Table) are listed the basic DRO parameters.
|
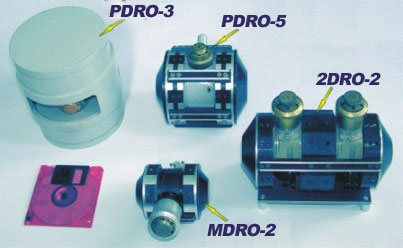 |
| Type of device |
F, GHz |
P, W |
Efficiency,% |
| Continuous-wave mode |
|
|
|
|
| Pulse mode |
|
|
|
|
| Miniaturized DROs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
C) Ka-band low voltage pulse magnetron
It is intended for use as microwave-power oscillator in short-range radar stations, i.e., in stationary radars to make on-line observations of a parameter situation on an airfield (runways), in mobile radar facilities to detect moving objects at short distances. The power it produces in a pulse mode varies between 400 W and 1 kW at an anode voltage of 4 kV. Its efficiency is ≈ 10 % and the mechanical tuning comes up to 2 %. Duty cycle is 1000.
|
|
|
|
D) X-band coaxial cold-cathode magnetron
This device has been put into full-scale production. For an anode voltage of 8 kV its output pulse power is between 10 and 25 kW and an efficiency
is equal to ≈30 %. Pulse duration ranges between 70 ns and 6 mcs. It has provided the basis for designing and developing the "Burevestnik-1"
radar to be used for state sea border surveillance.
|
|
|
|
E) High-vacuum film technologies
In order for high-vacuum film technologies to be introduced a double-beam multicrucible electron evaporator has been developed. It allows two or three, diverse-in-property materials to be sequentially or simultaneously evaporated in different film-producing processes including those involving implantation stimulation.The controlled size of a focus spot on the evaporation surface varies between 0.5 and 3 mm. The operational characteristics of the evaporator and its electron system are listed in Table below
|
 |
| Characteristics of evaporator and its electron-optical system |
Value |
| Maximum electron beam power |
5 êW |
| Maximum accelerating voltage |
6 êV |
| Controlled size of a focus spot on the evaporation surface |
0.5÷3 mm |
| Frequencies of longitudinal and transversal scanning with an amplitude of up to 30 mm |
0.1÷500 Hz |
| Gabarit length |
480 mm |
When using the evaporator in thin-film material production units the following parameters of the evaporation regime for
Al, Ni, Cu, Cr, Ti, Mo, Ta, Nb
are attained at an evaporation rate of 10÷15 A0/s: |
| The electron beam power is no more than |
2 kW |
Nonuniformity of coating density over surface
area is no more than |
0,5 % |
stable deposition time with no additional crucible
feed is no less than |
30 min |
Electron gun operation time prior to cathode replacement is
no less than |
250 h |
|
|
F) Automatic panoramic meter (APM-2)
It is designed to explore the characteristics of high-Q resonance systems, direct and inverse losses of quadripoles over a frequency
range of 37.5 to 140 GHz for the voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) varying between 1.1 and 5.0 with a minimum frequency tuning step of 0.1 to 0.2 MHz.
|